Escherichia coli (E. coli)
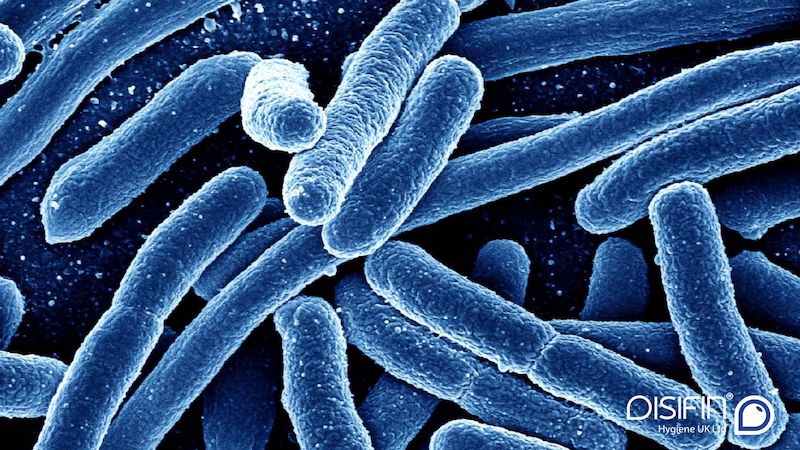
Escherichia coli (E. coli) bacteria normally live in the intestines of people and animals. Most E. coli are harmless and actually are an important part of a healthy human intestinal tract. However, some E. coli are pathogenic, meaning they can cause illness, either diarrhoea or illness outside of the intestinal tract.
The types of E. coli that can cause diarrhoea can be transmitted through contaminated water or food, or through contact with animals or persons.
E. coli consists of a diverse group of bacteria. Pathogenic E. coli strains are categorized into pathotypes.
Six pathotypes are associated with diarrhoea and collectively are referred to as diarrheagenic E. coli.
